Home » Positive Supports » Positive Behavior Support (PBS) » Positive Behavior Support and Preventing Challenging Behavior Using the Public Health Model
Positive Behavior Support and Preventing Challenging Behavior Using the Public Health Model
A key feature of positive behavior support is its emphasis on systems change. Considering larger organizational issues can be a helpful way to create a positive climate and prevent challenging behavior. One way to think about positive behavior support and systems change is to consider the public health disease prevention model. This triangle describes how the model is used to promote wellness and decrease the occurrence of challenging social behavior across three prevention levels. Data are collected at all three prevention levels to guide implementation efforts.
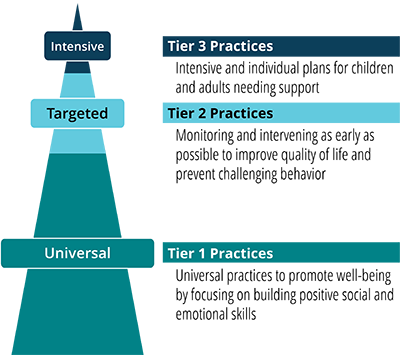
Tier 1 includes universal strategies for supporting all of the people living or working in a home, organization, or community setting. The goal of tier 1 is to implement strategies that will naturally prevent challenging behavior from occurring. These strategies are used to establish positive interactions within a setting by identifying, practicing, and reinforcing important social expectations and life values that are culturally relevant to the home, organization, or community setting.
Tier 2 strategies include early identification and intervention for minor problems that are occurring in a setting. The goal at the tier 2 level is to establish simple interventions that address the reason why minor challenging behavior is occurring. Simple problem-solving strategies are used to encourage communication, address mental health-related concerns, and change events or situations to decrease the likelihood of challenging behavior.
Tier 3 strategies are used to address chronic and severe social problems or mental illness. Positive behavior support planning can be used as a helpful process to support people who are experiencing greater challenges in their lives. Tier 3 includes person-centered planning, functional behavioral assessment, and function-based interventions.

